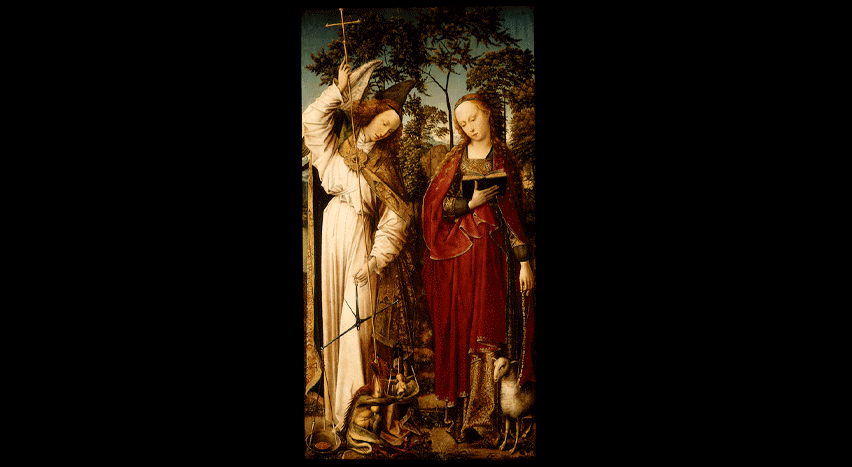
St. Michael the Archangel and St. Agnes
Oil on panel
Colijn de Coter
Flemish, c. 1455–d. 1538
Click on the links throughout the article to view additional artists’ works and reference material.
The construction of Colijn’s artistic career is based on three signed works, each representing the early, middle, and later phases of his style. Rogier van der Weyden’s compositional sense greatly influenced him, even though Colijn painted nearly half a century later. Colijn loved to explore the tactile qualities of the subjects he painted, while retaining the sculptural drapery effects characteristic of the art of this period. The influence of this artist’s works spread throughout his native Brussels in the late fifteenth and early sixteenth centuries.
Here, St. Michael is richly dressed in priestly embroidered silk robes similar to those found in van der Weyden’s works. The highly decorative cope is rendered so carefully that seemingly every gold thread of the garment is visible. The front trim of the cope has various unidentifiable saints within architectural niches while an elaborate gold quatrefoil morse clasps the garment together. Because St. Michael was originally part of a wing panel, de Coter breaks from van der Weyden’s frontal model and faces the character to the right in a contrapposto position that takes up nearly the entire width and height of the panel. The animation of his twisting pose is graphically emphasized by the long cross-staff that he uses to defeat the demon. One hand balances and thrusts the symbolic weapon into the demon’s throat, causing the flesh of its neck to protrude. Two fingers of the other hand carefully hold a ring in the fulcrum of the scales of justice.
The objects being weighed in the scales are of particular interest. On the right is a tiny seraph, identified by its six wings, representing a soul. Although Michael’s efforts will successfully prevent the demon from pulling the soul down, the object in the left pan of the scale far outweighs the soul and tips the scale to keep the symbolic seraph aloft (and safe from hell). What is it that could be providing such power to raise the soul out of evil’s grasp? At first glance it seems as if it might be representing the blood of Christ in a shallow dish. I John 1:7 says, “…and the blood of Jesus Christ his Son cleanseth us from all sin.” Closer examination reveals an image painted into the red oval shape (with pointed ends) that portrays a figure with a tiered tiara wearing a cope with a cross staff held in the left hand, the right hand across the front in a blessing position, and an arched throne behind. A narrow band also runs around the outer edge with marks that appear to represent letters. Altogether, the imagery presented identifies this object as a red wax seal in a lead dish—a type used by numerous secular and ecclesiastic rulers at this time but closest in shape and image to seals of a bishop or an abbot.
The presence of an ecclesiastic seal on St. Michael’s scale is virtually unknown outside of this image. Use of wax seals were commonplace throughout Europe in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries and were used to validate acts or protect and validate documents that were executed under an official’s name. The implied meaning behind the seal’s efficacy to counterbalance the soul and keep it from going to hell is remarkable. Its presence either authenticates the seal owner’s power to save souls (on Christ’s behalf) or is meant to show a certain bishop or ecclesiastic’s validation for Christ’s payment for mankind’s sins (as evidenced by Michael’s cross-staff overcoming the demon’s efforts to claim the soul). The specific identity of the ecclesiastic office represented by the seal is not readily apparent in the present image. Nothing on the seal identifies a specific person who owns it. Perhaps the original panel(s) that belonged with the present wings provided more information on whose seal and authority is being promoted with this iconography.
The other figure on the fused panel represents St. Agnes dressed in gorgeous brocade and scarlet fabric. Agnes actively reads her book while holding her symbolic, name-sake lamb on a gold-chained leash. The finery of dress is particularly evident and provides a pleasing balance to the ecclesiastic garb of Michael. De Coter’s composition delicately balances the swayed poses of the two figures as each gently holds their respective objects—Michael’s scale and Agnes’s leash.
Although no original documents are known for the present work and little period archival documentation survives on the artist himself, de Coter remains one of the most important and prolific painters from the Renaissance in Brussels. St. Michael the Archangel and St. Agnes is among his best preserved works and testifies to the ability and ingenuity of this artist.
John M. Nolan, Curator
Published in 2015